Ping a little
Breaking the myth in networking ….

Ping is named as Packet Internet Groper. It is a network software accountable for building network connections between systems. The word packet in PING would mean this software allows you to send packets over the internet which develops network connectivity.
The ping command first sends an echo request packet to an address, then waits for a reply.
It uses a series of Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) Echo messages to determine.
With the germination in technologies, there comes an addition to the myth table as well. Drawing you one of these in this article.
It is said that if system A can ping to a remote system B and a system C. Then the systems B and C can ping to each other. Of course, they can.

But is there a way we break this connection ?????…………………………Yes. We can unquestionably break this by the basic concepts of routing table rules. Let’s see how …

The task here is to create a network topology such that the A system can ping to B and C . Whereas, B and C cannot.
Basic terminologies to be dealt with in the task :
Routing Table :
The routing table contains the rules which allow or denies the system connectivity. We are going to create rules such that A system has an IP range to able to ping to both other systems. Similarly with the other two systems.

NetMask:
Netmask can be termed as a 32-bit binary mask used to divide an IP address into subnets and specify the network’s available hosts. A netmask of the system decides the network name also gives you data about how many ips in that given network are there. It's the combination of binary digits 1 and 0 behind the scene. 2^n where n = number of zeroes tells you the number of systems in the same network. It can also be expressed as /n, where n stands the no of bits containing 1 out of 32 bits.
We will bring changes in both of these to achieve our connectivity.
System A
Check the IP address using <ifconfig enp0s3>

Change the IP address using <ifconfig enp0s3 192.168.1.1/28>
Add the rule for new created IP < route add -net 192.168.1.0/30 enp0s3>

Why these changes?
In the first step, we changed the IP into 192.168.1.1/28 the /28 is the netmask here which suggests that this IP falls in the range of 4 systems ……(32 -28 =4). Secondly, we add the rule to the routing table so that these systems can connect to each other. Here the line 192.168.10/30 means, the IP range starts from 192.168.1.0 to 2 more systems i.e 192.168.1.2, 192.168.1.3.
Now we assign these two ips to other systems so that they can connect.
System B :


System C:


Conclusion :
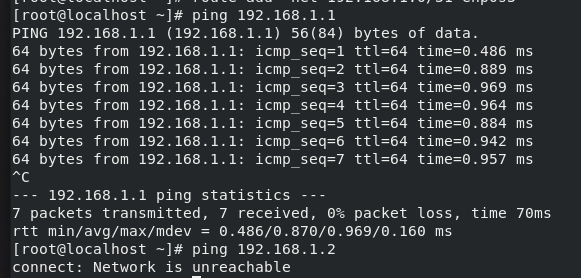
After all the changes have been made you can observe that system A can ping to the other two systems and likewise. Moreover, the systems B and C cannot ping each other because the routing table rules don't allow them to go beyond their network ips.
After the changes :
Ip of A = 192.168.1.1
Ip of B = 192.168.1.2
IP of C = 192.168.1.3